Unraveling the Enigma: A Dive into the World of Technetium
Technetium:
Technetium, a fascinating chemical element, occupies a unique place in the periodic table with its elusive nature and intriguing properties. Let's embark on a journey to uncover the mysteries surrounding this synthetic element.
Chemical Properties:
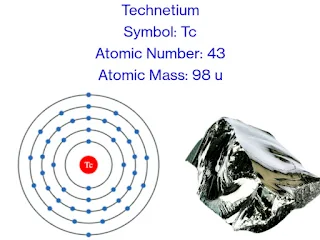
Symbol: Tc
Atomic Number: 43
Atomic Mass: 98
Electron Configuration: [Kr] 5s² 4d⁵
Valency: Various oxidation states, commonly +7
Chemical and Physical Properties:
Technetium exhibits diverse oxidation states, but its +7 state is the most stable. As a transition metal, it possesses characteristic metallic properties, including high melting and boiling points. Its radioactive nature adds an additional layer of complexity to its behavior.
Reactivity with Other Elements:
Technetium readily forms compounds with various elements, showcasing a versatile reactivity. Its interactions with oxygen, sulfur, and halogens contribute to the creation of numerous technetium compounds, each with distinct properties and applications.
Technetium Compounds:
Notable compounds include technetium dioxide (TcO₂) and technetium tetroxide (TcO₄), both playing roles in nuclear applications and research. Technetium forms a variety of coordination compounds due to its ability to bond with different ligands.
Occurrence and Production:
Primarily synthetic, technetium is a product of nuclear reactions. Trace amounts exist naturally, originating from spontaneous fission reactions in uranium ores. Isolation techniques involve sophisticated methods such as ion exchange chromatography.
Uses:
1. Medical Imaging:
Technetium-99m, a radioactive isotope, is widely used in nuclear medicine for diagnostic imaging, especially in bone scans and heart studies.
2. Research and Industry:
Its radioactive properties make technetium valuable for scientific research, tracer studies, and industrial applications.
3. Radiography:
Technetium-99m is employed in radiography for detecting fractures and abnormalities in bone structure.
Facts:
- Technetium Chemical element discovered in 1937 by Italian scientists Carlo Perrier and Emilio Segrè.
- Named after the Greek word "technetos," meaning "artificial," reflecting its synthetic origin.
- Technetium is the first element discovered without a naturally occurring isotope.
Conclusion:
Technetium, with its enigmatic qualities and applications, stands as a testament to humanity's ability to explore and harness the elements around us. From medical breakthroughs to industrial advancements, this synthetic element continues to shape the landscape of science and technology.
Also Read:
Neon | Descriptions, Chemical and Physical Properties, Uses & Facts
Nitrogen | Descriptions, Chemical and Physical Properties, Uses & Facts
Beryllium | Descriptions, Chemical and Physical Properties, Uses & Facts
Hydrogen | Difference between Blue and Green Hydrogen | Hydrogen Fuel









0 Comments