Silver: A Precious Metal with Timeless Value
Silver:
Silver, a captivating chemical element, has been treasured for centuries due to its unique properties and diverse applications. This blog explores the intricacies of silver, covering its chemical composition, properties, compounds, reactions, occurrence, production, and its role in various aspects of our lives, including its price, investment potential, and use in jewelry and other forms.
Chemical Element Basics:
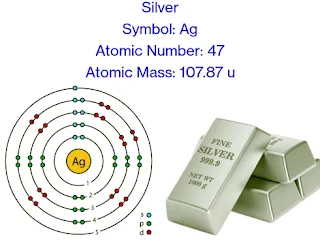
Symbol: Ag
Atomic Number: 47
Atomic Mass: 107.87 u
Electron Configuration: [Kr] 4d¹⁰ 5s¹
Valency: +1
Chemical and Physical Properties:
Silver possesses remarkable properties that contribute to its desirability:
- Excellent thermal and electrical conductivity.
- High reflectivity, making it invaluable in mirrors and reflective coatings.
- Malleability and ductility, allowing it to be shaped into intricate forms.
- Not easily tarnished, retaining its lustrous appearance over time.
Silver Compounds:
While silver is often found in its elemental form, it can also form various compounds, such as silver chloride (AgCl) and silver nitrate (AgNO₃), which have applications in photography, medicine, and as a reagent in chemical reactions.
Chemical Reactions with Other Elements:
Silver engages in chemical reactions with elements like sulfur and oxygen, forming compounds such as silver sulfide (Ag₂S) and silver oxide (Ag₂O).
Occurrence and Production:
Silver is commonly found in nature as a byproduct of the mining of other metals like lead, zinc, and copper. Its production involves extraction from ores through processes like cyanidation and smelting.
Silver in the Market:
Silver Price:
The price of silver is influenced by various factors, including demand, economic conditions, and geopolitical events.
Silver Spot Price:
This refers to the current market price for immediate delivery of silver.
Silver Coins and Bars:
Silver is widely used in the production of coins and bars, popular among investors seeking a tangible asset.
Silver in Everyday Life:
Silver Jewelry: The beauty and durability of silver make it a preferred choice for jewelry, ranging from intricate designs to modern styles.
Sterling Silver: A popular alloy, sterling silver, contains 92.5% silver and is widely used in jewelry and tableware.
Investing in Silver:
Kitco Silver: A reputable platform for tracking silver prices, offering information and tools for investors.
Investment Potential: Silver is often considered a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainties, attracting investors seeking diversification.
Uses of Silver:
1. Jewelry:
Silver's lustrous appearance and malleability make it a popular choice for crafting exquisite jewelry pieces. From earrings to necklaces, its timeless beauty appeals to various tastes and styles.
2. Currency:
Throughout history, silver has been used as a form of currency, minted into coins like the U.S. Silver Dollar or the Mexican Silver Libertad. While not as prevalent today, silver coins are still valued by collectors and investors.
3. Electronics:
Silver's exceptional conductivity of electricity and thermal properties make it a key component in electronic devices. From circuit boards to batteries, its use is integral to the functionality of many electronic gadgets.
4. Photography:
Silver's light-sensitive properties have long been utilized in photography. Silver halide crystals react to light exposure, forming the basis for traditional film photography. Although digital technology has advanced, silver's legacy remains in photographic archives.
5. Medical Applications:
Silver's antimicrobial properties find applications in medicine. Silver-based compounds are used in wound dressings, catheters, and medical coatings to prevent bacterial growth and infections.
6. Mirrors and Reflective Coatings:
Silver's high reflectivity makes it an ideal material for mirrors and reflective coatings in telescopes and other optical instruments, enhancing the clarity of images.
7. Catalysis:
Silver serves as a catalyst in various chemical reactions, particularly in the production of ethylene oxide, a crucial component in the manufacturing of plastics.
8. Water Purification:
Silver ions exhibit bactericidal properties, making silver an effective agent for purifying water. It is used in water filters and treatment processes to eliminate harmful microorganisms.
9. Culinary and Tableware:
Silver's antibacterial properties have led to its use in tableware, such as silverware and silver-lined vessels, contributing to the preservation of food and drink.
Fascinating Facts about Silver
1. Chemical Symbol and Atomic Number:
Silver is represented by the chemical symbol Ag, derived from the Latin word "argentum." Its atomic number is 47.
2. Noble Metal:
Silver, along with gold and platinum, is categorized as a noble metal due to its resistance to corrosion and oxidation.
3. Highest Electrical Conductivity:
Silver boasts the highest electrical conductivity among all elements, making it an essential component in electrical conductors.
4. Tarnish Resistance:
While silver can tarnish over time due to exposure to air and sulfur compounds, it tarnishes much more slowly than other metals, retaining its lustrous shine.
5. Abundance in Earth's Crust:
Silver is relatively abundant in the Earth's crust, occurring both in its elemental form and as part of various minerals.
6. Historical Significance:
Silver has played a significant role in various ancient civilizations as a form of currency, a symbol of wealth, and an integral part of religious ceremonies.
7. Isotopes:
Silver has two stable isotopes, Ag-107 and Ag-109, with Ag-107 being more prevalent in nature.
8. Photographic Legacy:
Silver's use in traditional photography has left an indelible mark on the art and science of capturing images, marking an era before the digital revolution.
Whether adorning our bodies, powering our electronic devices, or preserving our captured memories, silver's multifaceted nature and rich history continue to make it a captivating element in our lives.
Conclusion:
Silver's enduring allure lies not only in its aesthetic appeal but also in its versatility and industrial significance. As a precious metal, it continues to captivate markets, investors, and artisans alike, proving that its value transcends time and trends. Whether admired in jewelry, traded on the market, or integrated into cutting-edge technologies, silver remains a symbol of enduring value in our ever-evolving world.
Also Read:
Neon | Descriptions, Chemical and Physical Properties, Uses & Facts
Nitrogen | Descriptions, Chemical and Physical Properties, Uses & Facts
Beryllium | Descriptions, Chemical and Physical Properties, Uses & Facts
Hydrogen | Difference between Blue and Green Hydrogen | Hydrogen Fuel








0 Comments