Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments and Care
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. In this blog, we'll explore the key aspects of RA, including its symptoms, causes, treatment options, and self-care measures.
1. Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
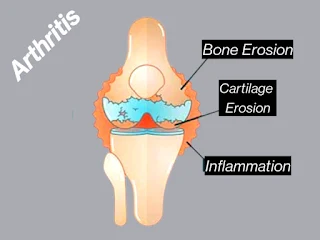
- RA is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and potential joint damage.
- It often affects joints on both sides of the body, such as the hands, wrists, and knees.
2. Common Symptoms of RA:
- Joint Pain and Swelling: Persistent pain and swelling in multiple joints, commonly the small joints of the hands and feet.
- Morning Stiffness: Stiffness that lasts for an extended period, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Fatigue: Generalized fatigue and weakness are common symptoms of RA.
3. Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Autoimmune Response: RA occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, the lining of the membranes that surround the joints.
Genetic Factors: There is a genetic predisposition to RA, but environmental factors also play a role in triggering the condition.
4. Treatment Options for RA:
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Medications like methotrexate and biologics target the immune system to slow down the progression of RA.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Provide relief from pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids: Can be prescribed for short-term relief of severe symptoms.
5. Arthritis in Fingers: A Common Manifestation:
- RA often affects the joints of the fingers, leading to deformities and limitations in hand function.
- Early intervention and proper treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent further joint damage.
6. Rheumatoid Factor (RF): A Diagnostic Marker:
- Rheumatoid factor is an antibody present in the blood of many people with RA.
- While its presence can aid in diagnosis, not all individuals with RA have elevated rheumatoid factor levels.
7. Inflammatory Arthritis: A Group of Disorders:
- RA falls under the category of inflammatory arthritis, a group of conditions characterized by joint inflammation.
- Other types include ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
8. Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Recognizing the Early Indicators:
- Early diagnosis is crucial for effective management. Look out for joint pain, stiffness, and swelling that persists over several weeks.
9. RA Self-Care: Empowering Patients:
Regular Exercise: Low-impact exercises help maintain joint flexibility and reduce stiffness.
Healthy Lifestyle: Proper nutrition, adequate rest, and stress management contribute to overall well-being.
Conclusion:
Rheumatoid Arthritis is a complex condition that requires a multidimensional approach to management. With early diagnosis, a tailored treatment plan, and proactive self-care, individuals with RA can lead fulfilling lives while effectively managing their symptoms. Consulting with healthcare professionals is key to developing a personalized strategy for living well with rheumatoid arthritis.








0 Comments